

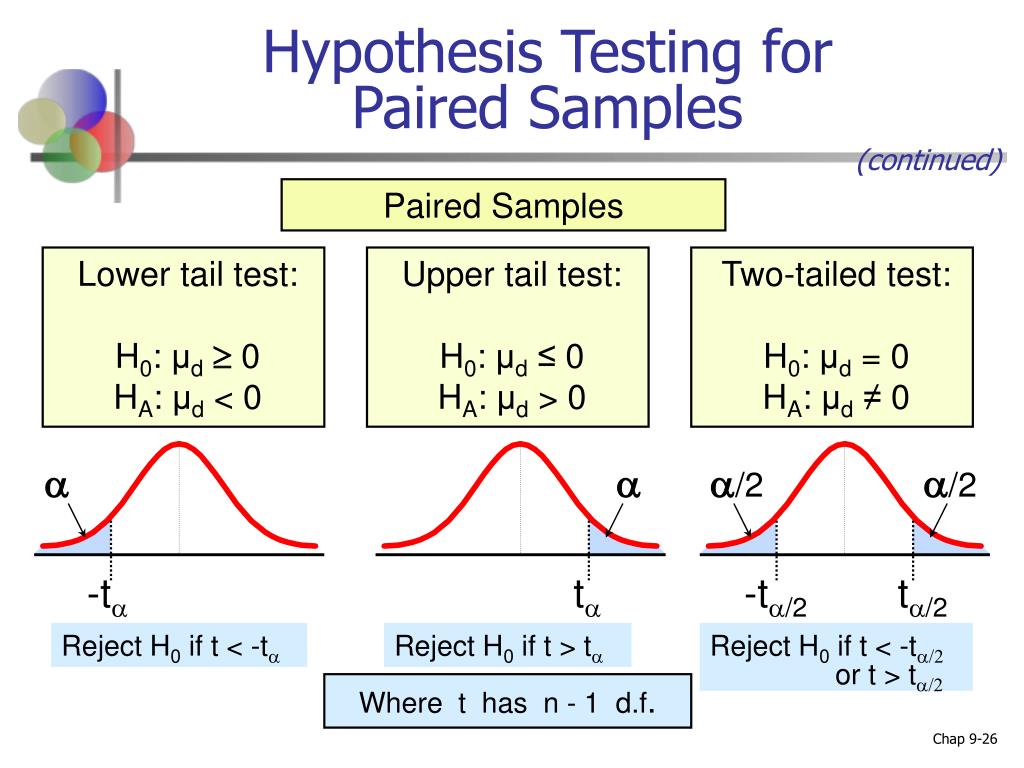
The histogram of the differences is key to seeing this - for a low p-value, it will be very narrow, and will be centred on a noticeably large value of the mean. The greater the mean of the group differences, and the lower the variance of the differences, the higher the calculated t value will be, leading to a lower p-value, possibly yielding a significant result. As we assume that all the data are distributed Normally, the spread of the histograms will be proportional to the variance of the samples within the groups, and the centre of the histograms will coincide with the means of the samples in the groups. This conveys a lot of useful information visually. To reload the same file after clearing the text areas, you would need to reload this webpage.Īt the bottom there is a graph that will display the histograms of both the groups and their difference.
Alternatively, you can choose a two-column CSV file to load - simply press on the choose file button below the clear Group 1 and Group 2 buttons. Group 1 and Group 2 must have the same number of samples. Please enter Group 1 and Group 2 values as comma separated numbers in the fields below. A worked example of carrying out the Paired Student's t-test can be found hereīelow is an online calculator that implements the Paired Student's t-test. If there are $N$ readings, samples 1 of the two datasets will be the reading from Patient 1 before and after treatment, samples 2 will be the readings from Patient 2 before and after treatment, and so on. For example, we could have the blood pressure readings for a group of patients before a certain medication is applied, and then the corresponding blood pressure readings for the same group of patients a few months after treatment. It thus requires that the two groups have the same number of samples. The Paired Student's t-test is a parametric test that determines whether two groups of matched (i.e. Cholesky decomoposition for Real Matrix.QR factorisation: Householder for Complex Matrix.QR factorisation: Householder for Real Matrix.QR factorisation: Gram-Schmidt for Complex Matrix.QR factorisation: Gram-Schmidt for Real Matrix.LU factorisation and Inverse of Complex Matrix.LU factorisation and Inverse of Real Matrix.Binary Matrix Operations for Complex Matrices.Binary Matrix Operations for Real Matrices.Error Function and Gaussian Distribution.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
